Even if you have been officially employed before, knowing the difference in the W-9 form and W-2 form is not guaranteed. Ranging in the employment type and tax details, W-2 vs W-4 vs W-9 are a lot to process. Today, let’s focus on the most common tax forms, i.e., W-9 vs W-2, and see how to deal with them.
W-2 vs W-9 Tax Form Types
Though similar in their outcome purpose, these forms have drastic differences when it comes to your employment type. And it’s essential to know W-9 vs W-2 when to use principles by heart.
What is a W-9 vs W2?
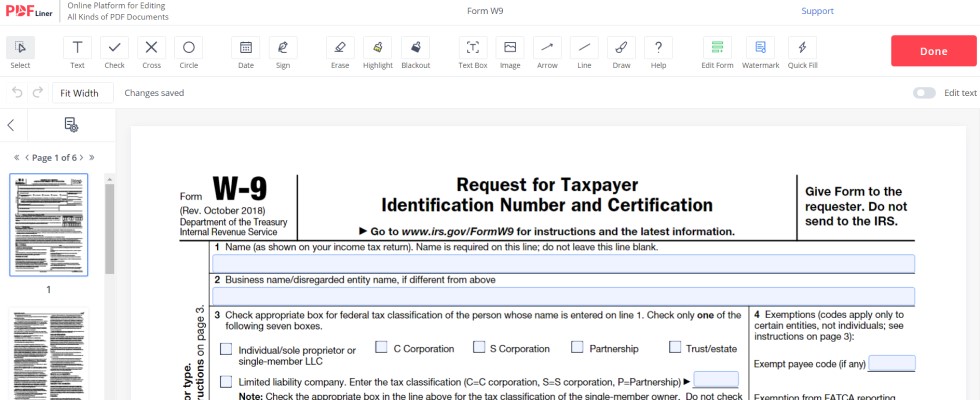
W-9 forms are used to track and subtract the federal tax from freelance employees. Contractors and other people who don’t work in the office are obliged to fill out the form to inform the IRS about their income. As for the tax itself, freelancers normally pay less due to their limited or absent social benefits package. It all gets a little more complex since you have to know the difference in W-9 vs W-2 vs 1099.
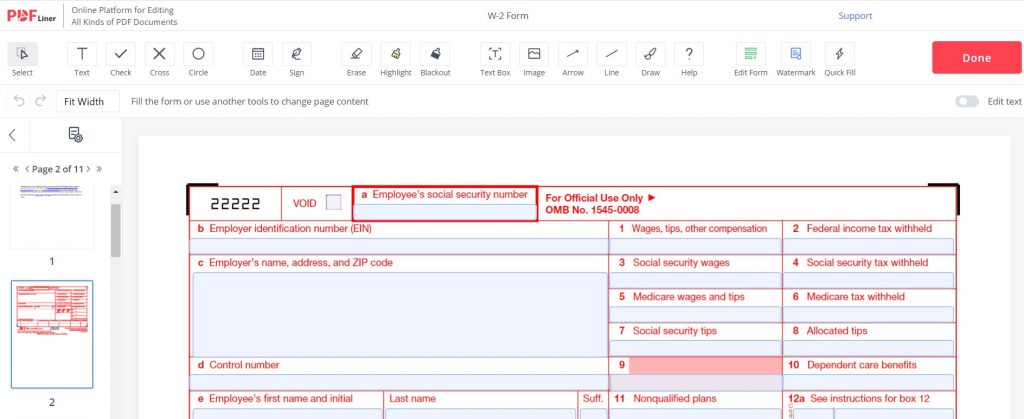
Sent either by post or handed directly, a W-2 form is designed for full-time employees. The form is meant to estimate your precise yearly income tax and federal tax. Normally, the tax is paid when your earnings exceed $600.
Both forms have equally beneficial traits that support an employee and protect their taxpayer’s rights. The responsibility of filling out and submitting the form is laid completely on the employee. Also, this rule applies to receive the form. In case you haven’t been handed and sent the form throughout the tax years, you have to contact the authorized bodies. Generally, you should contact a corresponding IRS department to request the form.
W-2 vs W-9 Employee Differences
People working under the W-2 form jurisdiction are considered more secure by the state than those who are independent contractors. Apparently, the form includes various information about your medical and social insurance, SSN, wages/salary, etc. This data provides you with full access to your social benefits package, enabling you to request a tax return at the beginning of the tax year.
Also, when you and the employer fill out W-9 vs W-2 vs 1099 IRS forms, you can decide how much federal tax to withdraw. Though it may not seem so at first, it’s a great opportunity to balance your annual tax payments. It allows you to add or subtract federal taxes depending on the outcome balance, thus improving your overall credit score.
As for W-9, it includes people whose employment is not full-time. Normally, the income tax is calculated, too, annually, but the employer doesn’t hold the federal tax responsibility. This way, people who work for hire aren’t bound by the employer’s 1099 submission.
On the other hand, the form, of course, has a more limited capacity. Not requiring your medical insurance information and other social benefits-related data, W-9 is much simpler. It doesn’t count in this data simply because the data is not charged or even monitored by the IRS. Besides, the IRS office may require your TIN or request its issuing to ensure proper identification. It’s important for the Revenue Service because there is no other legal entity that can confirm your work done, unlike W-2 employees who are bound by 1099.
Difference Between W-2 vs W-9

To sum it all up, let’s determine the main differences between the two.
First, the former tax form is issued for and requested to fill out by a full-time employer, whereas the latter is for freelancers. If you are officially employed (full-time) and you perform hourly jobs for wages, you are still the object of W-2, unless designated differently.
Second, W-2 includes much more precise information about your personal details (name, address, marital status, etc.), SSN, TIN, medical insurance, income, additional employment, and so on. All of them help the IRS determine your annual income tax and proceed to federal tax withdrawals. As for W-9, it is not too complicated and requires only general information to identify you and assess your annual contractor income.
Third, ‘What is the W-9 vs W-2 main difference?’ It’s that the full-time employment form is bound together with 1099. The latter is designed for your employer, who fills it out to see the annual federal tax balance and, therefore, make amends if necessary. While both of them are valid and essential for your tax withdrawal, the 1099 form is designed to compare your tax income rate, according to W-2, and that of your employer’s records. Contrastingly, freelancers have no legal obligations before the employer after a job is done. They are solely held responsible for their tax income assessment and don’t require any additional forms for their federal tax withdrawal.
Working on W-2 vs W-9
The two types of forms have similar purposes, so their filling out and submission procedures are alike. What a W-9 vs W-2 form needs is attention and time to fill out.
W-2
- Put in your general information, like name and employment type;
- Add your current employer’s identification information;
- Field 1 through 10 is focused on your income and wages, as well as types of taxes you pay regularly.
- Field 11 through 20 is about your benefits, like sick leave, sick wages, tips, etc.
W-9
- Verify your personal information;
- Complete the information about the business type and identify yourself using the SSN and TIN;
- Designate if you have a special withholding backup;
- Sign and date at the bottom.
Pros and Cons of W-2 vs W-9
The W-9 vs W-2 vs 1099 salary is different, but you have to understand that there is no ‘best option’. Both options are equally beneficial and suit different people’s needs. Take a look at the upsides and downsides of each.
| W-2 | |
| Pros | 1. Paid qualification training; 2. Medical insurance; 3. Paid sick leave; 4. Set commitment terms; 5. Employment security; 6. In-company growth. |
| Cons | 1. Expensive medical benefits for the employer; 2. Fixed work schedule; 3. Salary and wage limitations; 4. 2-week notice prior to dismissal; 5. Higher taxes; 6. Disability and single-parent employment limitations. |
As you can see, W-2 employment is a medal with two sides. When at work, an employee is heavily affected by control and supervision, leaving little room for flexibility. However, such limitations come with a good social security bonus package, including insurance, stable payments, etc.
| W-9 | |
| Pros | 1. Flexible and independent work schedule; 2. Lower taxes; 3. Possibility for employment for the impaired and single-caring parents; 4. Opportunity to combine working for different employers simultaneously; 5. Legal obligation exhaustion after a contract expires. |
| Cons | 1. Unstable income; 2. Limited or no social and medical benefits; 3. No supervision; 4. No qualification training. |
Contractors have the full freedom of time and work schedule alterations, as long as it complies with the agreement. However, W-9 employees are less socially protected by the company.
FAQs
If you have some more questions left about a W-9 form vs W-2 employment, take a look here.
Does W-9 pay more taxes vs W-2? What is a W-9 vs a W-2 tax payment requirement?
It’s hard to tell if people with a W-9 pay more taxes vs W-2 workers. Apparently, tax subtractions considerably depend on the income you declare. Normally, people with W-2 employment have a fixed tax index that is withheld from their payment monthly. In the long run, such individuals can predict and calculate almost the exact amount of money that they will have to pay.
As for freelancers, the tax is seemingly lower. However, if a contractor does jobs with over $500 each, their tax rate increases. This way, the taxes paid by W-9 workers are normally lower, but they can also exceed the taxes of W-2 employees at times.
How do I know W-2 vs W-9? Which one is the form for me?
The choice of your taxation form depends on the type of employment you have established. Normally, the situation should be clear if you work at home without going to an office. To receive more detailed information about your yearly tax payments, you need to contact the employer. They should provide you with all the necessary information and hand you W-2 if you’re full time.
What are the tax brackets W-9 vs W-2?
The tax rate for both of the forms is not stable. Each state determines its own rate, depending on the Taxation Law. Ranging between 10 and 37 percent, the figure may vary. You can find out the exact amount of tax by visiting your local taxation department’s website or contacting them directly via phone.